Canine Temporal Bone Anatomy. Notably the inferior alveolar nerve a branch of the mandibular nerve accesses the mandible foramen and runs frontward providing sensation to the lower set of teethAt the mental foramen it branches into the incisive and mental nerves. Cookies allow us to analyze and store information such as the characteristics of your device as well as certain personal data eg IP addresses navigation usage or geolocation data unique identifiers.
Paired sinuses within the body of the maxilla. Dorsal nuchal lines of the occipital bone and mastoid part of the temporal bone. Plays an important role in controlling mandibular movement and is sometimes called the canine tooth or the eye.
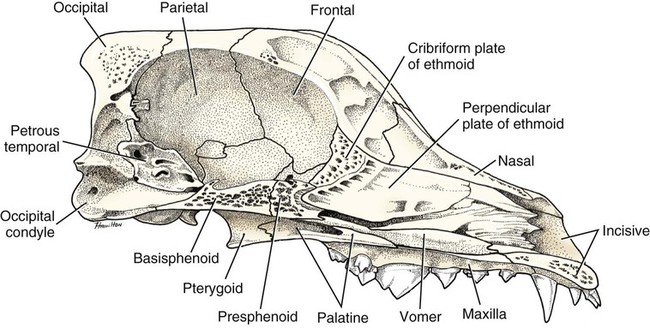
Atlas of anatomy on x-ray images of the dog.
Extends and raises the neck. Through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone by the olfactory nerves. In this article we will look at the anatomy and clinical importance of the mandible. IMAIOS and selected third parties use cookies or similar technologies in particular for audience measurement.
