Brachialis Muscle Tendon Mri Anatomy. The median nerve arises from the medial C8 and T1 nerve roots and lateral C5-C7 nerve roots cords of the brachial plexus and extends down the arm medial to the biceps and brachialis muscles and anterior to the brachial artery. Muscle strain is an injury to the musculotendinous junction.
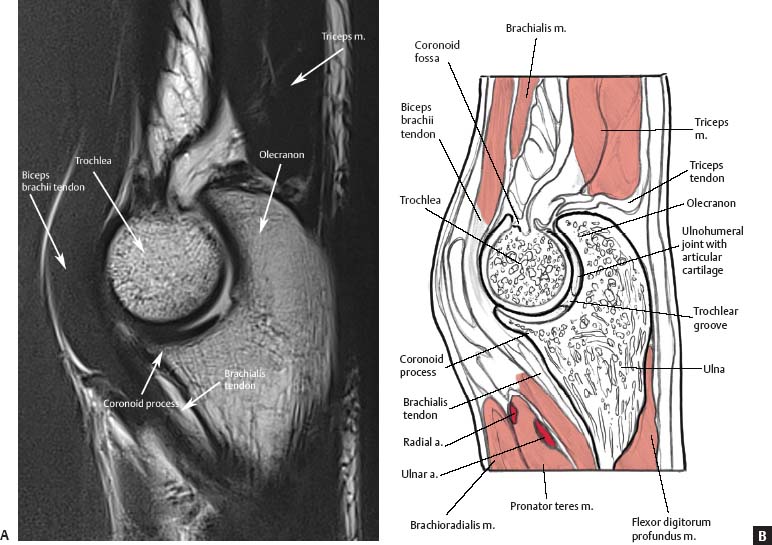
The tendon of the Brachioradialis muscle cannot be seen or well palpated which makes this reflex a bit tricky to elicit. The tendon crosses the radius thumb side of the lower arm approximately 10 cm proximal to the wrist. Ultrasound of the Elbow Date of Study.
A muscle slip the axillary arch varying from 7 to 10 cm in length and from 5 to 15 mm in breadth occasionally springs from the upper edge of the latissimus dorsi about the middle of the posterior fold of the axilla and crosses the axilla in front of the axillary vessels and nerves to join the under surface of the tendon of the pectoralis major the coracobrachialis or the fascia over.
The shoulder joint also known as the glenohumeral joint is a ball and socket joint with the most extensive range of motion in the human body. MRI of the upper extremity anatomy - Atlas of the human body using cross-sectional imaging We created an anatomical atlas of the upper limb an interactive tool for studying the conventional anatomy of the shoulder arm forearm wrist and hand based on an axial magnetic resonance of the entire upper limb. The coracobrachialis muscle lies deep to the biceps brachii in the arm. The biceps tendon is a strong supinator of the forearm and serves as a weak elbow flexor.
